
News
发布日期:2023-09-26 浏览次数:3471 来源:WOLF-LAB杨广成
EI CCNP培训课程学习笔记-BGP建立邻居过程及路由发布详解

【WOLF-LAB网络技术实验室】思科认证EI CCNP培训课程循环开班,联系网站客服预约免费试听!
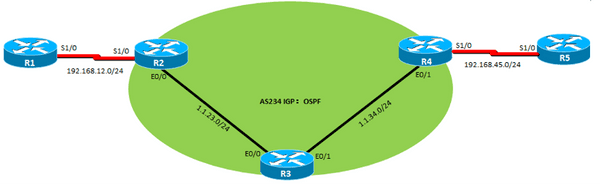
接口ip地址请结合课程视频的地址规划,实验拓扑如上图所示:
R1预配置: interface Loopback0 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 interface Serial1/0 ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0 | R2预配置: interface Loopback0 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0 interface Serial1/0 ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0 |
1、直连建立邻居:
(1)在R1和R2之间通过直连接口建立iBGP邻居,AS 100,sh ip bgp nei, 观察默认的keepalive/holddown间隔;
R1: router bgp 100 bgp router-id 1.1.1.1 neighbor 192.168.12.2 remote-as 100 | R2: router bgp 100 bgp router-id 2.2.2.2 neighbor 192.168.12.1 remote-as 100 |
R1:show ip bgp neighbor BGP neighbor is 192.168.12.2, remote AS 100, internal link BGP version 4, remote router ID 2.2.2.2 BGP state = Established, up for 00:00:07 Last read 00:00:07, hold time is 180, keepalive interval is 60 seconds Neighbor capabilities: Route refresh: advertised and received(old & new) Address family IPv4 Unicast: advertised and received | |
(2) 将R1的keepalive/holddown interval 60/150,手工修改R2的keepalive/holddown interval 20/180,观察两个路由器的间隔分别为多少,依据结果,得出间隔计算的结论。
R1: router bgp 100 timers bgp 60 150
| R1:show ip bgp neighbor BGP neighbor is 192.168.12.2, remote AS 100, internal link BGP version 4, remote router ID 2.2.2.2 BGP state = Established, up for 00:00:12 Last read 00:00:12, hold time is 150, keepalive interval is 50 seconds Configured hold time is 150, keepalive interval is 60 seconds |
R2: router bgp 100 timers bpg 20 180
| R2:show ip bgp neighbor BGP neighbor is 192.168.12.1, remote AS 100, internal link BGP version 4, remote router ID 1.1.1.1 BGP state = Established, up for 00:00:54 Last read 00:00:03, hold time is 150, keepalive interval is 20 seconds Configured hold time is 180, keepalive interval is 20 seconds |
注意:需要清除BGP邻居,再看现象。
结论:
a、建邻居的两端,先协商Hold时间,Hold时间保持一致,Hold时间为两端的最小值。
b、keepalive时间 > 三分之一的Hold时间,取三分之一的Hold时间作为keepalive时间。
c、keepalive时间 <= 三分之一的Hold时间,keepalive时间不变。
2、Debug ip bgp , 然后 clear ip bgp *,观察邻居建立的过程。
R1: debug ip bgp *Feb 11 14:41:28.139: BGP: 192.168.12.2 went from Idle to Active *Feb 11 14:41:28.139: BGP: 192.168.12.2 open active, delay 6115ms R1# *Feb 11 14:41:34.255: BGP: 192.168.12.2 open active, local address 192.168.12.1 *Feb 11 14:41:34.295: BGP: 192.168.12.2 went from Active to OpenSent *Feb 11 14:41:34.295: BGP: 192.168.12.2 sending OPEN, version 4, my as: 100 *Feb 11 14:41:34.299: BGP: 192.168.12.2 send message type 1, length (incl. header) 45 *Feb 11 14:41:34.355: BGP: 192.168.12.2 rcv message type 1, length (excl. header) 26 *Feb 11 14:41:34.355: BGP: 192.168.12.2 rcv OPEN, version 4 *Feb 11 14:41:34.355: BGP: 192.168.12.2 rcv OPEN w/ OPTION parameter len: 16 *Feb 11 14:41:34.355: BGP: 192.168.12.2 rcvd OPEN w/ optional parameter type 2 (Capability) len 6 *Feb 11 14:41:34.359: BGP: 192.168.12.2 OPEN has CAPABILITY code: 1, length 4 *Feb 11 14:41:34.359: BGP: 192.168.12.2 OPEN has MP_EXT CAP for afi/safi: 1/1 *Feb 11 14:41:34.359: BGP: 192.168.12.2 rcvd OPEN w/ optional parameter type 2 (Capability) len 2 *Feb 11 14:41:34.359: BGP: 192.168.12.2 OPEN has CAPABILITY code: 128, length 0 *Feb 11 14:41:34.359: BGP: 192.168.12.2 OPEN has ROUTE-REFRESH capability(old) for all address-families *Feb 11 14:41:34.359: BGP: 192.168.12.2 rcvd OPEN w/ optional parameter type 2 (Capability) len 2 *Feb 11 14:41:34.359: BGP: 192.168.12.2 OPEN has CAPABILITY code: 2, length 0 *Feb 11 14:41:34.363: BGP: 192.168.12.2 OPEN has ROUTE-REFRESH capability(new) for all address-families *Feb 11 14:41:34.363: BGP: 192.168.12.2 went from OpenSent to OpenConfirm *Feb 11 14:41:34.363: BGP: 192.168.12.2 went from OpenConfirm to Established |
解析:初始阶段,双方都是idle状态,等待连接重试时间到期后,双方进入active状态,并且双方各自回退一个随机delay时间,delay小的路由器,delay到期后,将主动发起TCP连接,delay大的路由器在收到TCP连接请求后,将回到idle状态后进入到connect状态,TCP连接建立完后,双方进入OpenSent状态,在这状态中,双发互相发送open消息,并且侦听来自邻居的open消息,如果接收到的open消息没有差错,则发送keepalive消息并设置keepalive定时器,协商保持时间,根据对方的AS号,确定连接是内部的还是外部的,并且迁移到OpenConfirm状态,在OpenConfirm状态下,一旦收到keepalive消息,则进入到establish状态,establish状态后,即双方已经建立BGP邻居,随即双方交换update包。
3、利用loopback口建立iBGP邻居:
(1)将BGP中的neighbor 指向对方的环回口,打开debug ip bgp,在R1上指一条默认路由到R2,在R2指一条静态路由到R1 ip route 1.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 s1/0, 观察debug 输出,R1有没有主动发起TCP连接?
解析:R1不会主动发起TCP连接,因为R1上是默认路由,默认路由是不会主动发起TCP连接请求的。
(2)R2有没有主动发起TCP连接?
解析:R2会主动发起TCP连接,但是到R1上TCP源检测失败。
(3) R2上的主动TCP连接是否成功建立了连接?为什么?在R2上增加一条命令使R2-R1的邻居关系能够建立,这时建立起的TCP连接,谁是TCP高端口,谁是TCP 179?为什么?通过sh tcp brief证实。如果需要双方都能互相主动发起TCP连接请求,该如何设置?
解析:R2会主动发起TCP连接,但是到R1上TCP源检测失败。因为R2发起连接的时候用的源地址是出接口地址,而R1要检测TCP发起的连接的源地址是2.2.2.2,所以R1将会拒绝R2发起的TCP连接请求。
R2上增加如下命令: router bgp 100 neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source loopback 0 |
R1:show tcp brief TCB Local Address Foreign Address (state) 641F24BC 1.1.1.1.179 2.2.2.2.52585 ESTAB //看到R2的高端口发向R1的179端口 |
如果双方都可以发起TCP连接请求,需要在R1上做如下配置: R1: ip route 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 s1/0 router bgp 100 neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source loopback 0 |
4、EBGP邻居的建立:将R2的AS区域设为AS 200,使用直连接口建立eBGP邻居关系。
R1: router bgp 100 bgp router-id 1.1.1.1 neighbor 192.168.12.2 remote-as 200 | R2: router bgp 200 bgp router-id 2.2.2.2 neighbor 192.168.12.1 remote-as 100 |
5、将上述需求4的直连eBGP邻居no掉。在R1 R2之间使用loopback接口能建立eBGP邻居。
方法一配置: R1: Router bgp 100 neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 200 neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source loopback 0 neighbor 2.2.2.2 disable-connected-check R2: Router bgp 200 neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100 neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source loopback 0 neighbor 1.1.1.1 disable-connected-check | 方法二配置: R1: Router bgp 100 neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 200 neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source loopback neighbor 2.2.2.2 ebgp-multihop R2: Router bgp 200 neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100 neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source loopback 0 neighbor 1.1.1.1 ebgp-multihop |
6、还原以上R1 R2 路由器,将R1设为AS 100, R2 R3 R4设为AS234,R5设为AS500,在R1和R2之间建立直连接口的eBGP邻居,在R2和R4之间用环回口建立iBGP邻居关系,在R4 R5间用直连口建立eBGP邻居关系。
R1: interface loopback 0 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 interface s1/0 ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0 router bgp 100 bgp router-id 1.1.1.1 neighbor 192.168.12.2 remote-as 234 | R5: interface loopback 0 ip address 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.0 interface s1/0 ip address 192.168.45.5 255.255.255.0 router bgp 500 bgp router-id 5.5.5.5 neighbor 192.168.45.4 remote-as 234 |
R2: interface loopback 0 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0 interface s1/0 ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0 interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 1.1.23.2 255.255.255.0
router ospf 1 router-id 2.2.2.2 network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 1.1.23.2 0.0.0.0 area 0
router bgp 234 bgp router-id 2.2.2.2 neighbor 192.168.12.1 remote-as 100 neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 234 neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source loopback 0 | R4: interface loopback 0 ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.0 interface Ethernet0/1 ip address 1.1.34.4 255.255.255.0 interface s1/0 ip address 192.168.45.4 255.255.255.0
router ospf 1 router-id 4.4.4.4 network 1.1.34.4 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 area 0
router bgp 234 bgp router-id 4.4.4.4 neighbor 192.168.45.5 remote-as 500 neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 234 neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source loopback 0 |
R3: interface loopback 0 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.0 interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 1.1.23.3 255.255.255.0 interface Ethernet0/1 ip address 1.1.34.3 255.255.255.0 router ospf 1 router-id 3.3.3.3 network 1.1.23.3 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 1.1.34.3 0.0.0.0 area 0 | |
7、在R1上将192.168.12.0/24和1.1.1.0/24 network进BGP,在R5上将192.168.45.0/24和5.5.5.0/24 network进BGP。注意BGP宣告的特征,此时BGP进程下是no auto-summary。如果R1上此时是通过network 1.0.0.0能否将1.1.1.0/24的路由引入BGP表?
R1: router bgp 100 network 192.168.12.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 1.0.0.0 | R5: router bgp 500 network 192.168.45.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 5.5.5.0 mask 255.255.255.0 |
R1:show ip bgp Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i | |
解析:在no auto-summary情况下,network后面的网段和掩码必须和路由表中的条目精确匹配才能引入。此时通过network 1.0.0.0,不能引入1.1.1.0/24这条路由。应该是 network 1.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0,才可以将1.1.1.0/24这条路由引入R1的BGP表。
8、在R4上 sh ip bgp观察从R1引入的两条bgp路由,和R2上有什么区别?为什么?理解iBGP邻居之间传递路由时的默认行为。
R2:show ip bgp Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 1.1.1.0/24 192.168.12.1 0 0 100 i r> 192.168.12.0 192.168.12.1 0 0 100 i |
R4:show ip bgp Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path * i1.1.1.0/24 192.168.12.1 0 100 0 100 i * i192.168.12.0 192.168.12.1 0 100 0 100 i |
解析:R4上的BGP路由不优。IBGP邻居之间传递路由,默认情况下,下一跳是不变的,由于R4上的BGP路由下一跳是192.168.12.1,而R4上没有去往192.168.12.1的路由,所以BGP路由不优,从而不会提交给路由表,也不会传给自己的BGP邻居。
9、如果希望R5能收到192.168.12.0/24和1.1.1.0/24这条路由,在R2上应如何设置?如何配置,可以让BGP路由优化;观察R5的BGP表,理解eBGP之间传递路由时的默认行为。
R2: router bgp 234 neighbor 4.4.4.4 next-hop-self //R2向R4邻居传递路由的时候,下一跳改为2.2.2.2. |
R4:show ip bgp Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *>i1.1.1.0/24 2.2.2.2 0 100 0 100 i *>i192.168.12.0 2.2.2.2 0 100 0 100 i |
R5:show ip bgp //EBGP邻居之间传递路由,下一跳改变。 Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 1.1.1.0/24 192.168.45.4 0 234 100 i *> 192.168.12.0 192.168.45.4 0 234 100 I / |
10、此时R5收到此条路由,能否ping通R1的环回口?
解析:无法ping通R1环回口,由于R3没有运行BGP,所以并没有1.1.1.1的路由,数据包达到R3时由于没有路由,将会被丢弃。
11、在R4上开启BGP同步,观察R5的路由表,R5还能否收到R1引入的两条路由?
R4: router bgp 234 synchronization |
解析:R5不能收到R1始发的两条路由。R4上开启BGP同步。同步的要求:从IBGP邻居收到的路由,路由表中也得有对应的此路由,此时R4的路由表中并没有192.168.12.0/24和1.1.1.0/24这两条路由,所以,不符合同步的要求,这两条IBGP路由不优,也就不能提交路由表,亦不能传递给R5。
12、在R2上将192.168.1.0/24和1.1.1.0/24重分布进OSPF,此时R5能否收到R1的环回口路由?能否ping通此路由?在R2上也开启同步,在R4上将192.168.45.0/24和5.5.5.0/24重分布进OSPF,此时R1能否收到R5的环回口路由?理解同步所要实现的目的 — BGP早期用于解决路由黑洞的方法。
R2 router ospf 1 redistribute connected subnets redistribute bgp 234 subnets | R4:show ip bgp Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path r>i1.1.1.0/24 2.2.2.2 0 100 0 100 i r>i192.168.12.0 2.2.2.2 0 100 0 100 i |
R4 router ospf 1 redistribute connected subnets redistribute bgp 234 subnets | R2:show ip bgp Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path r>i5.5.5.0/24 4.4.4.4 0 100 0 500 i r>i192.168.45.0 4.4.4.4 0 100 0 500 i |
解析:在R2和R4开启同步以后,要求从IBGP邻居收到的路由,路由表中也得有对应的此路由。因此在R4和R2上把路由重分布进OSPF,通过过OSPF传递到R2和R4上,路由表中有对应的路由,也就符合同步的要求了,此时可以看到R2和R4的BGP中的路由优化。
WOLFLAB官方微信:17316362402
WOLFLAB官方QQ:2569790740
思科认证CCNP培训、学习、考试联系WOLF-LAB网络技术实验室